It Supports Database Migration
AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) helps you migrate databases to AWS quickly and securely. The source database remains fully operational during the migration, minimizing downtime to applications that rely on the database. The AWS Database Migration Service can migrate your data to and from the most widely used commercial and open-source databases.
AWS Database Migration Service supports homogeneous migrations such as Oracle to Oracle, as well as heterogeneous migrations between different database platforms, such as Oracle or Microsoft SQL Server to Amazon Aurora. With AWS Database Migration Service, you can also continuously replicate data with low latency from any supported source to any supported target. For example, you can replicate from multiple sources to Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) to build a highly available and scalable data lake solution. You can also consolidate databases into a petabyte-scale data warehouse by streaming data to Amazon Redshift. Learn more about the supported source and target databases.
Introduction to AWS Database Migration Service (1:33)
Use cases
Homogeneous Database Migrations
In homogeneous database migrations, the source and target database engines are the same or are compatible—like Oracle to Amazon RDS for Oracle, MySQL to Amazon Aurora, MySQL to Amazon RDS for MySQL, or Microsoft SQL Server to Amazon RDS for SQL Server. Since the schema structure, data types, and database code are compatible between the source and target databases, this kind of migration is a one-step process. You create a migration task with connections to the source and target databases, and then start the migration with the click of a button. AWS Database Migration Service takes care of the rest. The source database can be located in your own premises outside of AWS, running on an Amazon EC2 instance, or it can be an Amazon RDS database. The target can be a database in Amazon EC2 or Amazon RDS.


Verizon is a global leader delivering innovative communications and technology solutions. "Verizon is helping our customers build a better, more connected life. As part of this journey, we are undergoing a major transformation in our database management approach, moving away from expensive, legacy commercial database solutions to more efficient and cost-effective options. Testing of Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL showed better performance over standard PostgreSQL residing on Amazon EC2 instances, and the AWS Database Migration Service and Schema Conversion Tool were found effective at identifying areas for data-conversion that required special attention during migration." - Shashidhar Sureban, Associate Director, Database Engineering, Verizon.
Heterogeneous Database Migrations
In heterogeneous database migrations, the source and target databases engines are different—like in the case of Oracle to Amazon Aurora, Oracle to PostgreSQL, or Microsoft SQL Server to MySQL migrations. In this case, the schema structure, data types, and database code of source and target databases can be quite different, requiring a schema and code transformation before the data migration starts. That makes heterogeneous migrations a two-step process. First, use the AWS Schema Conversion Tool to convert the source schema and code to match that of the target database. Then use the AWS Database Migration Service to migrate data from the source database to the target database. All required data types will be automatically converted during the migration. The source database can be located in your own premises outside of AWS, running on an Amazon EC2 instance, or it can be an Amazon RDS database. The target can be a database in Amazon EC2 or Amazon RDS.


Trimble is a global leader in telematics solutions. They had a significant investment in on-premises hardware in North America and Europe running Oracle databases. Rather than refresh the hardware and renew the licenses, they opted to migrate the databases to AWS. They ran the AWS Schema Conversion Tool to analyze the effort, and then migrated their complete database to a managed PostgreSQL service on Amazon RDS. "Our projections are that we will pay about one quarter of what we were paying in our private infrastructure." -Todd Hofert, Director of Infrastructure Operations, Trimble.
Development and Test
AWS Database Migration Service can be used to migrate data both into and out of the cloud for development purposes. There are two common scenarios. The first is deploying development, test, or staging systems on AWS to take advantage of the cloud's scalability and rapid provisioning. This lets developers and tester use copies of real production data, then copy updates back to the on-premises production system. The second scenario is when development systems are on-premises (often on personal laptops) and you migrate a current copy of an AWS Cloud production database to these on-premises systems—either once or continuously. You can avoid a disruption to existing DevOps processes while ensuring the up-to-date representation of your production system.

Database Consolidation
You can use AWS Database Migration Service to consolidate multiple source databases into a single target database. This can be done for homogeneous and heterogeneous migrations, and you can use this feature with all supported database engines. The source databases can be located in your own premises outside of AWS, running on an Amazon EC2 instance, or it can be an Amazon RDS database. The source databases can also be spread across different locations. For example, one of the source databases can be in your own premises outside of AWS, while the second one in Amazon EC2, and the third one in an Amazon RDS database. The target can be a database in Amazon EC2 or Amazon RDS.

Continuous Data Replication
You can use AWS Database Migration Service to perform continuous data replication. Continuous data replication has a multitude of use cases including Disaster Recovery instance synchronization, geographic database distribution and Dev/Test environment synchronization. You can use DMS for both homogeneous and heterogeneous data replications for all supported database engines. The source or destination databases can be located in your own premises outside of AWS, running on an Amazon EC2 instance, or it can be an Amazon RDS database. You can replicate data from a single database to one or more target databases or consolidate and replicate data from multiple databases to one or more target databases.
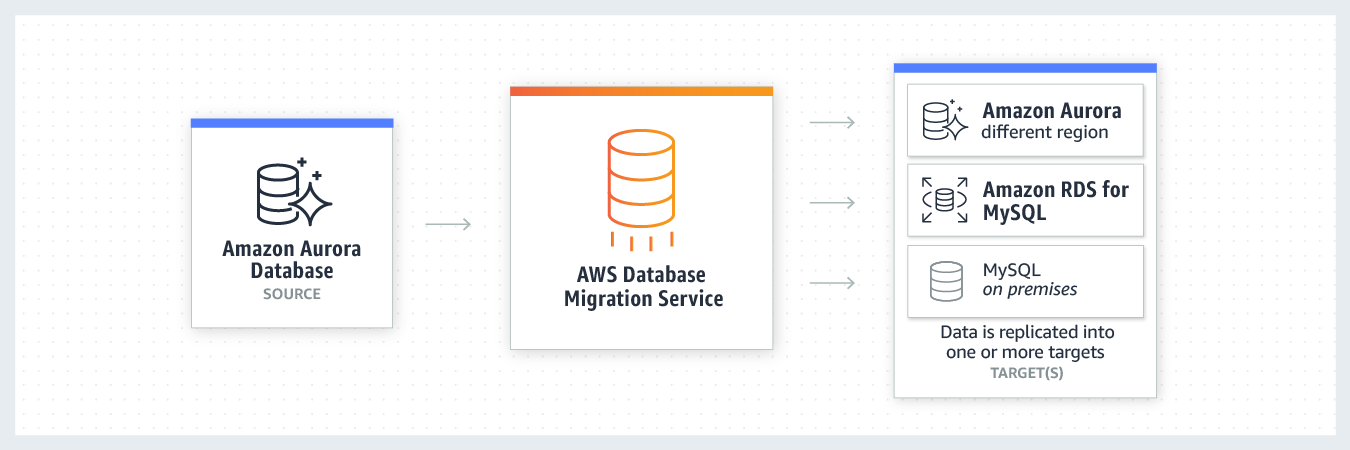

The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) processes hundreds of thousands of Veterans Appeals each year. "Our appeals processing system, VACOLS, includes 20 million records stored in an Oracle 11g database. The system is more than 20 years old and is in the process of being modernized. During this time, we need to ensure that the data is securely replicated into the cloud for safekeeping. We're using AWS DMS to replicate the database into an RDS Oracle database in AWS GovCloud, in a Multi-AZ deployment. This setup ensures that VACOLS data is preserved, secured, and highly available in the cloud, which is a serious win for VA and for our Veterans, who rely on us for the safeguarding of their information." – Alan Ning, Site Reliability Engineer, U.S. Digital Service.
patriciociagooract.blogspot.com
Source: https://aws.amazon.com/dms/
0 Response to "It Supports Database Migration"
Post a Comment